
If you’ve ever watched a spy movie, you’ve probably seen something like multi-factor authentication (MFA) in action. Think about those high-security vaults that require a keycard, a PIN, and maybe even a retina scan to open. While real-world MFA isn’t quite as dramatic, the idea is the same: adding multiple layers of security makes it much harder for unauthorized people to break in.
In today’s digital world, passwords alone just don’t cut it anymore when it comes to protecting your online accounts. Hackers have countless ways to steal or guess passwords, which is why multi-factor authentication (MFA) has become one of the best tools for beefing up security. But how does MFA actually work, and why is it so important? Let’s break it down in simple terms.
Table of Contents
What Is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security method that requires two or more forms of proof to verify your identity before granting access to an account. Instead of just entering a password, you’ll need to provide additional evidence that you’re the rightful owner of the account.
For example, when logging into your email, you might be asked to enter a code sent to your phone. That extra step makes it much harder for hackers to get in, even if they somehow manage to steal your password.
The Three Types of Authentication Factors
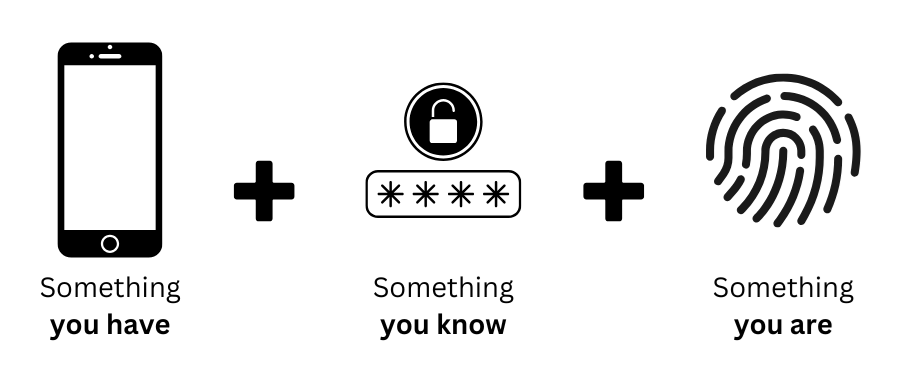
MFA works by combining different categories of authentication factors. There are three main types:
Something You Know
This is information that only you should know, such as:
- A password
- A PIN (Personal Identification Number)
- Answers to security questions
Something You Have
This involves a physical device that belongs to you, like:
- Your smartphone (used for SMS codes or authentication apps)
- A hardware security key (like a USB device)
- A smart card
Something You Are
This refers to unique biological traits that identify you, such as:
- Fingerprints
- Facial recognition
- Voice recognition
A strong MFA system requires at least two of these categories to ensure better protection.
How MFA is Different from Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
People often confuse MFA with Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), but there’s a subtle difference.
- 2FA requires exactly two factors from two different categories. For example: A password (Something You Know) + a code from an authentication app (Something You Have).
- MFA allows for more flexibility and can include two or more factors. For instance: A password, a fingerprint scan, and a security key.
MFA offers stronger protection than 2FA because more factors mean more layers of security.
Why is MFA So Important?
MFA is crucial because passwords alone aren’t enough to keep your accounts safe. Here’s why:
- Passwords Can Be Stolen – Hackers use phishing emails, data breaches, or malware to steal passwords.
- People Reuse Passwords – Many users make the mistake of using the same password across multiple accounts. If one gets leaked, others are at risk.
- Brute-Force Attacks – Cybercriminals use automated tools to guess passwords.
Even if you think your password is strong, it’s not foolproof. That’s where MFA comes in—it reduces the risk by adding an extra layer of security. Even if a hacker manages to get your password, they still need another authentication factor, which they likely don’t have.
Bonus Tip: Use a Password Manager
While MFA is a game-changer for account security, it’s also important to ensure your passwords themselves are as strong as possible. A great way to do this is by using a password manager. Password managers generate and store complex, unique passwords for each of your accounts, so you don’t have to remember them all. This eliminates the temptation to reuse passwords and makes your accounts even harder to crack. Pairing a password manager with MFA gives you a powerful one-two punch against hackers.
Read more about password managersHow MFA Works in Real Life
Let’s say you’re logging into your bank account from a new device. Here’s how MFA would protect you:
- You enter your username and password.
- The system asks for additional verification.
- You receive a one-time code on your phone or use a fingerprint scan to confirm it’s really you.
- Once the extra step is completed, you gain access.
This process ensures that even if someone else knows your password, they still can’t get in without your second or third authentication factor.
Different Ways to Use MFA
There are several ways MFA can be implemented. Some common methods include:
1. SMS or Email Codes
A one-time passcode (OTP) is sent to your phone or email. While this is better than just a password, it’s not the most secure option because hackers can intercept SMS messages or break into your email.
2. Authentication Apps
Apps like Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or Duo generate time-sensitive codes. This method is more secure than SMS since the codes are only stored on your device.
3. Hardware Security Keys
A small physical device (like YubiKey) that must be plugged in or tapped to authenticate. This is one of the most secure options available.
4. Biometrics
Using fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice authentication. This is common in smartphones and high-security environments.
Each method has its pros and cons, but using an authenticator app or a security key is generally safer than relying on SMS-based MFA.
How to Enable MFA on Your Accounts
Most online services offer MFA, but in many cases, you’ll need to enable it yourself. Some platforms now enforce MFA by default when you create a new account, particularly for services that handle sensitive information such as banking, email, or cloud storage. If MFA isn’t automatically enabled, it’s important to make activating it a standard part of your routine whenever you sign up for a new account anywhere.
Here’s how to set up MFA in general:
- Go to your account’s security settings (Google, Facebook, Microsoft, etc.).
- Find the Multi-Factor Authentication (or 2FA) option.
- Choose your preferred authentication method (app, SMS, security key, etc.).
- Follow the setup instructions to link your device.
- Test it to make sure everything works correctly.
Once set up, MFA will ask for an extra verification step whenever you sign in from an unknown device or location.
Final Thoughts
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is one of the simplest and most effective ways to protect your online accounts from hackers. By requiring multiple verification steps, it makes unauthorized access much harder.
If you haven’t set up MFA yet, take a few minutes to enable it on your important accounts especially emails, banking, and social media. A little extra security can save you from a lot of trouble.
