
Picture yourself browsing the internet at home or using a public Wi-Fi network at a café. You visit websites, watch videos, or shop online. Unbeknownst to you, your Internet Service Provider (ISP), the websites you visit, and even the café’s network administrator could be monitoring your activity and location. This happens because your device communicates directly with the online services you access. A Virtual Private Network (VPN) acts as a shield, creating a secure pathway to protect your data and privacy.
This article breaks down the fundamentals of VPNs, how they function, and why they’re useful. We’ll avoid complex terminology and focus on a clear, approachable explanation. Whether you’re a casual user or someone concerned about online privacy, this guide will help you understand how VPNs contribute to safer internet use.
Table of Contents
VPN Basics
Before diving into specifics, let’s start with the core principles. A VPN’s primary role is to protect your online activity and location, but how does it achieve this? Below, we’ll outline the foundational concepts that make VPNs a go-to tool for privacy-conscious users.
What Is a VPN?
A VPN is a service that establishes an encrypted tunnel between your device and a remote server run by the VPN provider. Once connected, all data traveling through this tunnel is scrambled, making it unreadable to outsiders. Additionally, a VPN masks your IP address (the unique identifier tied to your device) and replaces it with one from the VPN server. This hides your real location and helps keep your online activities private.
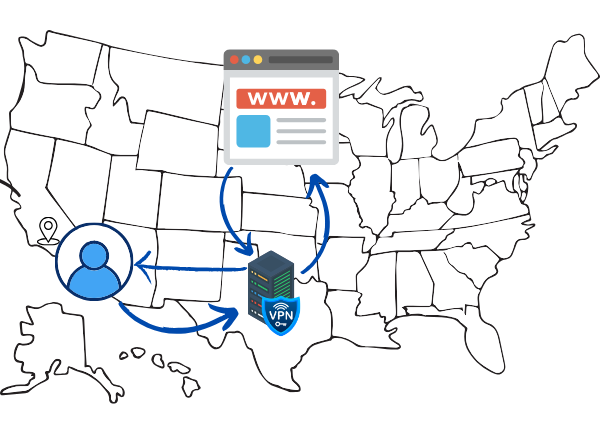
Why Does Location Matter?
Your IP address reveals your approximate geographic location. Websites and services use this data to customize content, but it can also be exploited for tracking or advertising. By connecting to a VPN server in another region or country, you obscure your true location. This makes it harder for advertisers, websites, or your ISP to link your browsing habits to your real-world identity or residence. Many users appreciate this feature for maintaining anonymity online.
Use our tool to check your IP & locationHow a VPN Works
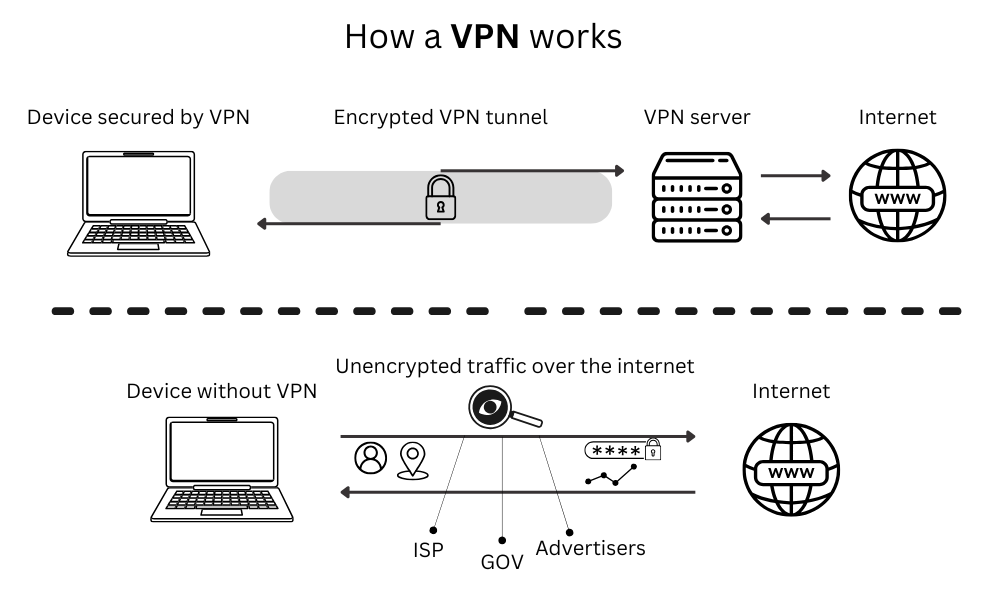
Understanding the mechanics of a VPN doesn’t require a technical background. Let’s break down the process step by step, focusing on how encryption and server routing combine to protect your data.
Building the Tunnel
When you turn on your VPN, your device connects to the VPN provider’s server. The two then negotiate a secure channel using encryption protocols. Think of encryption as a secret code: only your device and the VPN server can translate the data. Even if someone intercepts it, like your ISP or a hacker on a public network, they’ll see only scrambled information.
Masking Your IP Address
Once the tunnel is active, your online traffic appears to originate from the VPN server’s IP address instead of your own. For example, if you visit a website, it sees the VPN server’s location, not yours. While the site might still detect your browser type or device details, your physical location remains hidden. This process is key to maintaining privacy and bypassing regional restrictions.
Benefits of Using a VPN
VPNs offer more than just privacy by addressing multiple pain points for modern internet users. Below are the key advantages that make VPNs a popular choice for both casual browsing and specialized needs.
Better Privacy
A VPN adds a layer of anonymity by preventing your ISP from logging your browsing history. Websites see the VPN server’s IP address, not yours, and advertisers struggle to tie your activity to your real identity. This is especially valuable for those who want to minimize data collection.
Safer Public Wi-Fi
Public networks in places like airports or coffee shops are often insecure. Hackers on the same network could intercept unencrypted data, such as login credentials. A VPN encrypts your traffic, making it much harder for others to spy on your activity.
Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) public service announcement warns citizens to be careful when using wireless hotel networks for remote work. “Increase in Telework from Hotels Could Pose a Cyber Security Risk for Guests” the announcement reads.
Accessing Global Content
Streaming platforms and websites sometimes restrict content based on location. A VPN lets you bypass these restrictions by making it seem like you’re browsing from another country. Note, however, that this may violate some platforms’ terms of service.
Avoiding ISP Throttling
Some ISPs intentionally slow down specific activities, like video streaming. Since a VPN encrypts your traffic, your ISP can’t easily identify what you’re doing, which may help avoid speed throttling.
Drawbacks and Things to Consider
While VPNs are powerful tools, they aren’t flawless. Let’s explore potential limitations and factors to weigh before committing to a service.
Slower Speeds
Encryption and rerouting traffic through a remote server can slightly slow your connection. While premium VPNs minimize this lag, expect a minor speed reduction compared to a direct connection without a VPN.
A good way to test your connection speed is by using a Speedtest service by Ookla.
Trusting Your VPN Provider
Your VPN provider can see your internet activity, so choosing a reputable service is critical. Research their logging policies, since ideally they should keep no records of your data. Free VPNs often monetize through ads or data collection, so read their terms carefully.
Legal and Regional Issues
Some countries restrict or ban VPNs. Always check local laws before using one. Additionally, streaming services like Netflix may block VPN servers, requiring you to switch servers or providers.
Costs
Most reliable VPNs charge a subscription fee to maintain secure infrastructure. Free options exist, but they often come with compromises like slower speeds, invasive ads, or selling data gathered from your internet activities.
Conclusion
At its core, a VPN is a privacy tool that reroutes your internet traffic through an encrypted tunnel to a remote server. This hides your IP address, secures your data, and lets you browse as if you’re in another location. While VPNs offer significant benefits, like enhanced privacy and access to global content, they aren’t perfect. Slower speeds and reliance on your VPN provider’s trustworthiness are trade-offs to consider.
By selecting a reputable VPN that aligns with your needs, you can enjoy greater security and freedom online. Whether you’re protecting sensitive data or streaming shows from abroad, a VPN is a valuable addition to your digital toolkit.
